What is MVVM?
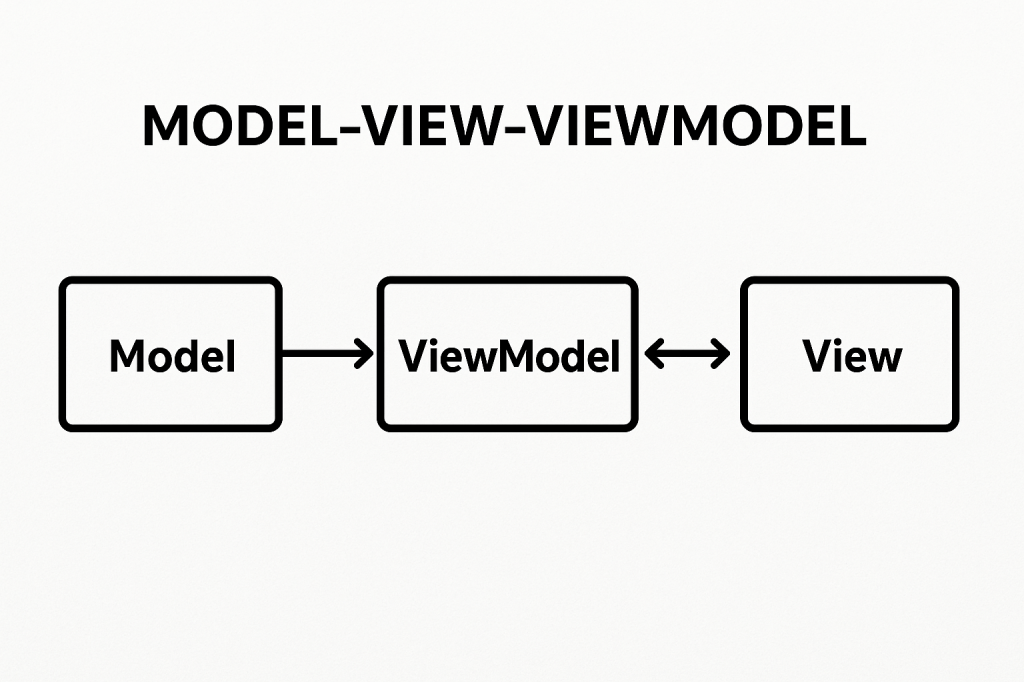
Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) is a software architectural pattern that helps organize code by separating the user interface (UI) from the business logic. It acts as an evolution of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern, designed to make applications more testable, maintainable, and scalable. MVVM is particularly popular in applications with complex user interfaces, such as desktop and mobile apps.
A Brief History
MVVM was introduced by Microsoft around 2005 as part of the development of Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF). The goal was to provide a clean separation between the UI and underlying application logic, making it easier for designers and developers to collaborate. Over time, the pattern has spread beyond WPF and is now used in many frameworks and platforms, including Xamarin, Angular, and even some JavaScript libraries.
Main Components of MVVM
MVVM is built on three main components:
Model
- Represents the data and business logic of the application.
- Responsible for managing the application state, retrieving data from databases or APIs, and applying business rules.
- Example: A
Customerclass containing fields likeName,Email, and methods for validation.
View
- Represents the user interface.
- Displays the data and interacts with the user.
- Ideally, the view should contain minimal logic and be as declarative as possible.
- Example: A screen layout in WPF, Android XML, or an HTML template.
ViewModel
- Acts as a bridge between the Model and the View.
- Handles UI logic, state management, and provides data in a format the View can easily consume.
- Exposes commands and properties that the View binds to.
- Example: A
CustomerViewModelexposing properties likeFullNameor commands likeSaveCustomer.
Benefits of MVVM
- Separation of Concerns: UI code is decoupled from business logic, making the system more maintainable.
- Improved Testability: Since the ViewModel doesn’t depend on UI elements, it can be easily unit tested.
- Reusability: The same ViewModel can be used with different Views, increasing flexibility.
- Collaboration: Designers can work on Views while developers work on ViewModels independently.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Cleaner and more organized code structure.
- Reduces duplication of logic across UI components.
- Makes it easier to scale applications with complex user interfaces.
Disadvantages
- Can introduce complexity for smaller projects where the overhead is unnecessary.
- Learning curve for developers new to data binding and command patterns.
- Requires careful planning to avoid over-engineering.
When Can We Use MVVM?
MVVM is best suited for:
- Applications with complex or dynamic user interfaces.
- Projects requiring strong separation of responsibilities.
- Teams where designers and developers work closely together.
- Applications needing high test coverage for business and UI logic.
Real World Example
Consider a banking application with a dashboard displaying account balances, recent transactions, and quick actions.
- Model: Manages account data retrieved from a server.
- View: The dashboard screen the user interacts with.
- ViewModel: Provides observable properties like
Balance,TransactionList, and commands such asTransferMoney.
This allows changes in the Model (like a new transaction) to automatically update the View without direct coupling.
Integrating MVVM into Our Software Development Process
- Identify UI Components: Break down your application into Views and determine the data each needs.
- Design ViewModels: Create ViewModels to expose the required data and commands.
- Implement Models: Build Models that handle business rules and data access.
- Apply Data Binding: Bind Views to ViewModels for real-time updates.
- Testing: Write unit tests for ViewModels to ensure correctness without relying on the UI.
- Iterate: As requirements change, update ViewModels and Models while keeping the View lightweight.
Recent Comments