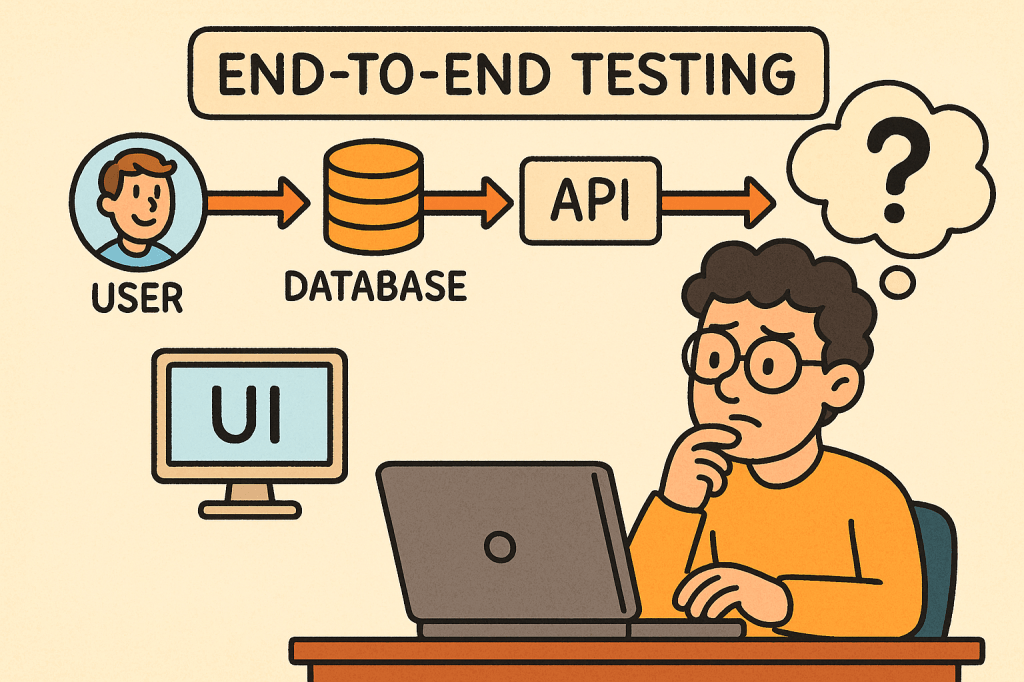
In today’s fast-paced software world, ensuring your application works seamlessly from start to finish is critical. That’s where End-to-End (E2E) testing comes into play. It validates the entire flow of an application — from the user interface down to the database and back — making sure every component interacts correctly and the overall system meets user expectations.
What is End-to-End Testing?
End-to-End testing is a type of software testing that evaluates an application’s workflow from start to finish, simulating real-world user scenarios. The goal is to verify that the entire system — including external dependencies like databases, APIs, and third-party services — functions correctly together.
Instead of testing a single module or service in isolation, E2E testing ensures that the complete system behaves as expected when all integrated parts are combined.
For example, in an e-commerce system:
- A user logs in,
- Searches for a product,
- Adds it to the cart,
- Checks out using a payment gateway,
- And receives a confirmation email.
E2E testing verifies that this entire sequence works flawlessly.
How Does End-to-End Testing Work?
End-to-End testing typically follows these steps:
- Identify User Scenarios
Define the critical user journeys — the sequences of actions users perform in real life. - Set Up the Test Environment
Prepare a controlled environment that includes all necessary systems, APIs, and databases. - Define Input Data and Expected Results
Determine what inputs will be used and what the expected output or behavior should be. - Execute the Test
Simulate the actual user actions step by step using automated or manual scripts. - Validate Outcomes
Compare the actual behavior against expected results to confirm whether the test passes or fails. - Report and Fix Issues
Log any discrepancies and collaborate with the development team to address defects.
Main Components of End-to-End Testing
Let’s break down the key components that make up an effective E2E testing process:
1. Test Scenarios
These represent real-world user workflows. Each scenario tests a complete path through the system, ensuring functional correctness across modules.
2. Test Data
Reliable, representative test data is crucial. It mimics real user inputs and system states to produce accurate testing results.
3. Test Environment
A controlled setup that replicates the production environment — including databases, APIs, servers, and third-party systems — to validate integration behavior.
4. Automation Framework
Automation tools such as Cypress, Selenium, Playwright, or TestCafe are often used to run tests efficiently and repeatedly.
5. Assertions and Validation
Assertions verify that the actual output matches the expected result. These validations ensure each step in the workflow behaves correctly.
6. Reporting and Monitoring
After execution, results are compiled into reports for developers and QA engineers to analyze, helping identify defects quickly.
Benefits of End-to-End Testing
1. Ensures System Reliability
By testing complete workflows, E2E tests ensure that the entire application — not just individual components — works as intended.
2. Detects Integration Issues Early
Since E2E testing validates interactions between modules, it can catch integration bugs that unit or component tests might miss.
3. Improves User Experience
It simulates how real users interact with the system, guaranteeing that the most common paths are always functional.
4. Increases Confidence Before Release
With E2E testing, teams gain confidence that new code changes won’t break existing workflows.
5. Reduces Production Failures
Because it validates real-life scenarios, E2E testing minimizes the risk of major failures after deployment.
Challenges of End-to-End Testing
While E2E testing offers significant value, it also comes with some challenges:
- High Maintenance Cost
Automated E2E tests can become fragile as UI or workflows change frequently. - Slow Execution Time
Full workflow tests take longer to run than unit or integration tests. - Complex Setup
Simulating a full production environment — with multiple services, APIs, and databases — can be complex and resource-intensive. - Flaky Tests
Tests may fail intermittently due to timing issues, network delays, or dependency unavailability. - Difficult Debugging
When something fails, tracing the root cause can be challenging since multiple systems are involved.
When and How to Use End-to-End Testing
E2E testing is best used when:
- Critical user workflows need validation.
- Cross-module integrations exist.
- Major releases are scheduled.
- You want confidence in production stability.
Typically, it’s conducted after unit and integration tests have passed.
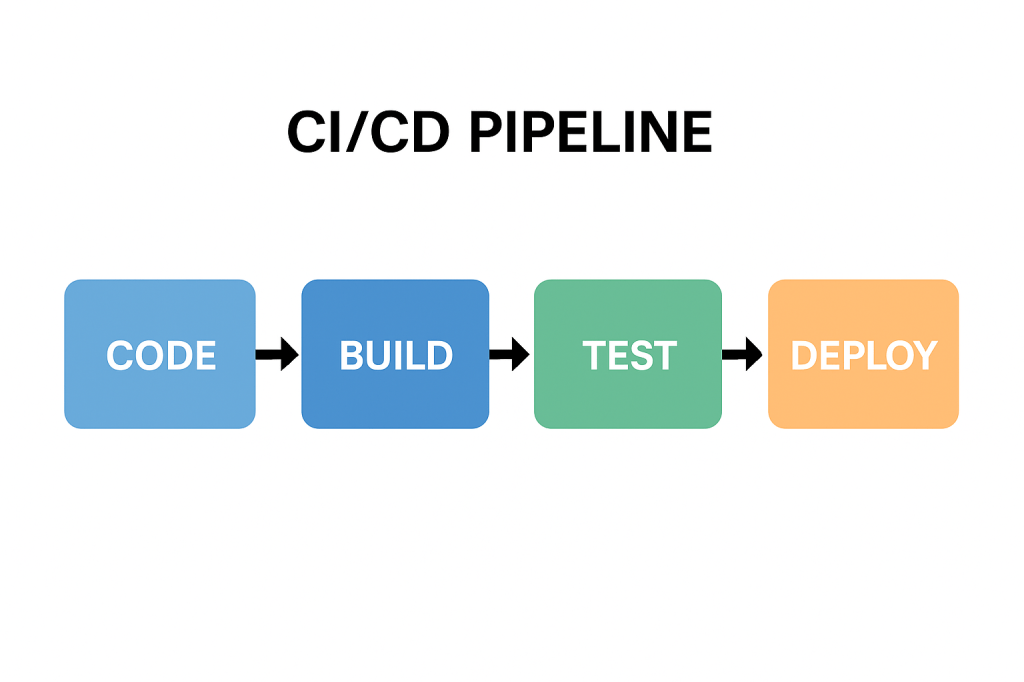
In Agile or CI/CD environments, E2E tests are often automated and run before deployment to ensure regressions are caught early.
Integrating End-to-End Testing into Your Software Development Process
Here’s how you can effectively integrate E2E testing:
- Define Key User Journeys Early
Collaborate with QA, developers, and business stakeholders to identify essential workflows. - Automate with Modern Tools
Use frameworks like Cypress, Selenium, or Playwright to automate repetitive E2E scenarios. - Incorporate into CI/CD Pipeline
Run E2E tests automatically as part of your build and deployment process. - Use Staging Environments
Always test in an environment that mirrors production as closely as possible. - Monitor and Maintain Tests
Regularly update test scripts as the UI, APIs, and workflows evolve. - Combine with Other Testing Levels
Balance E2E testing with unit, integration, and acceptance testing to maintain a healthy test pyramid.
Conclusion
End-to-End testing plays a vital role in ensuring the overall quality and reliability of modern software applications.
By validating real user workflows, it gives teams confidence that everything — from UI to backend — functions smoothly.
While it can be resource-heavy, integrating automated E2E testing within a CI/CD pipeline helps teams catch critical issues early and deliver stable, high-quality releases.
Recent Comments