When working with logic, programming, or digital systems, we often need a way to clearly represent how different conditions lead to specific outcomes. This is where truth tables come in. They provide a simple and structured way to visualize logical relationships.
What is a Truth Table?

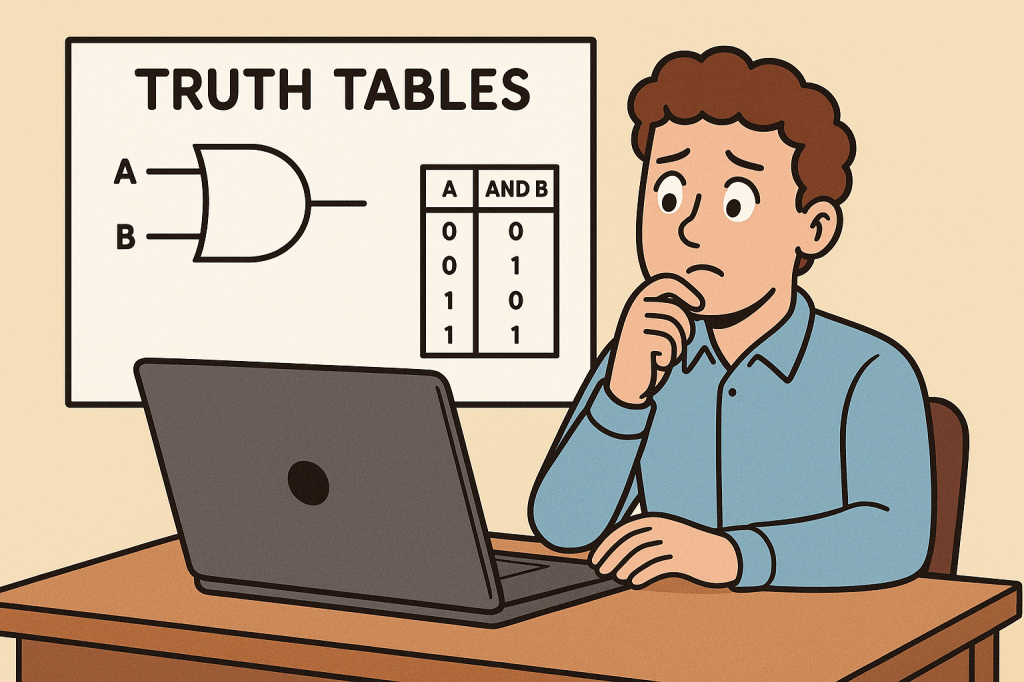
A truth table is a tabular representation of all possible values of logical variables and the results of applying logical operations to them. Each row of the table shows one possible combination of input values and the corresponding output.
For example, in Boolean logic, variables can only take values of true (1) or false (0). A truth table lists all combinations of true and false values and shows the resulting output for a given expression or logic gate.
How Do We Use Truth Tables?
Truth tables are used to:
- Evaluate logical expressions step by step.
- Verify the correctness of logical statements.
- Design digital circuits by showing how inputs affect outputs.
- Understand how multiple conditions combine in programming.
By laying everything out in a table, it becomes easier to see the exact behavior of a logical rule.
When Do We Need Truth Tables?
You will typically need a truth table when:
- Designing or analyzing digital circuits (AND, OR, NOT, XOR gates, etc.).
- Checking logical equivalence between different expressions.
- Debugging conditional logic in software programs.
- Learning the basics of Boolean algebra in computer science education.
In short, whenever there are multiple conditions that can combine in different ways, a truth table helps make sense of them.
How Do We Create a Truth Table?
- Identify the variables: Determine the logical inputs (e.g., A, B).
- List all combinations: For two variables, there are 4 combinations; for three, there are 8; in general, for n variables, there are 2^n combinations.
- Apply the operation: Write down the output of the logical expression for each row.
- Fill the table: Once all rows are complete, the truth table fully represents the logic.
Example for the AND operator with two variables A and B:
| A | B | A AND B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Real World Use Cases of Truth Tables
- Digital Electronics: Truth tables define the behavior of circuits used in computers, calculators, and smartphones.
- Programming: When combining multiple conditions in an
ifstatement, truth tables help ensure correctness. - Database Queries: Logical conditions like
WHERE A AND BorWHERE A OR Bcan be validated using truth tables. - Artificial Intelligence: Rule-based expert systems use truth tables to represent decisions.
- Mathematics & Logic: Used to prove logical equivalences and theorems.
Conclusion
Truth tables may seem simple, but they form the foundation of logical reasoning in computer science. Whether you’re writing a program, learning Boolean algebra, or designing digital circuits, understanding truth tables is essential. By systematically showing every possible combination of inputs and outputs, truth tables make complex logic easier to understand, verify, and apply in the real world.
Recent Comments